OPERATORS IN C++
C++ has a rich set of operators. Operators are the term used to describe the action to be taken between two data operands. Expressions are made by combining operators between operands.
C++ supports six types of operators:
- Arithmetical operators
- Relational operators
- Logical operators
- Bitwise operators
- Precedence of operators
- Special operators
- Escape sequence
Arithmetical operators
An operator that performs an arithmetic (numeric) operation such as +, -, *, /, or % is called arithmetic operator. Arithmetic operation requires two or more operands. Therefore these operators are called binary operators. The Table shows the arithmetic operators:
Operator Meaning Example Answer
+ addition 8+5 13
- subtraction 8-5 3
* multiplication 8*5 40
/ division 10/2 5
% modulo 5%2 1
Relational operators
The relational operators shown in Table 2.3 are used to test the relation between two values. All relational operators are binary operators and therefore require two operands. A relational expression returns zero when the relation is false and a non-zero when it is true.
Operator Meaning Example
== Equal to 5==5
!= Not equal to 5!=7
> Greater than 7>5
< Less than 8<9
>= Greater than or equal to 8>=8
<= Less than or equal to 9<=9
Logical operators
The (!) operator is the C++ operator to perform the Boolean operation NOT. It has only one operand, located at its right, and the only thing that it does is to inverse the value of it, producing false if its operand is true and true if its operand is false. Basically, it returns the opposite Boolean value of evaluating its operand. Logical operators of C++.
Operator Meaning
&& Logical AND
|| Logical OR
! Logical NOT
Bitwise Operators
In C++ programming language, bitwise operators are used to modify the bits of the binary pattern of the variables.
operator equivalent Description
& AND Bitwise AND
| OR Bitwise Inclusive OR
^ XOR Bitwise Exclusive OR
~ NOT Unary complement (bit inversion)
<< SHL Shift Left
>> SHR Shift Right
Precedence of Operators
In case of several operators in an expression, we may have some doubt about which operand is evaluated first and which later. For example, let us take following expression:
a = 5 + 7 % 2
Here we may doubt if it really means:
A = 5 + (7 % 2) // with a result of 6, or
a = (5 + 7) % 2 // with a result of 0
The correct answer is the first of the two expressions, with a result of 6. Precedence Introduction to C++ order of some operators in C++ programming language.
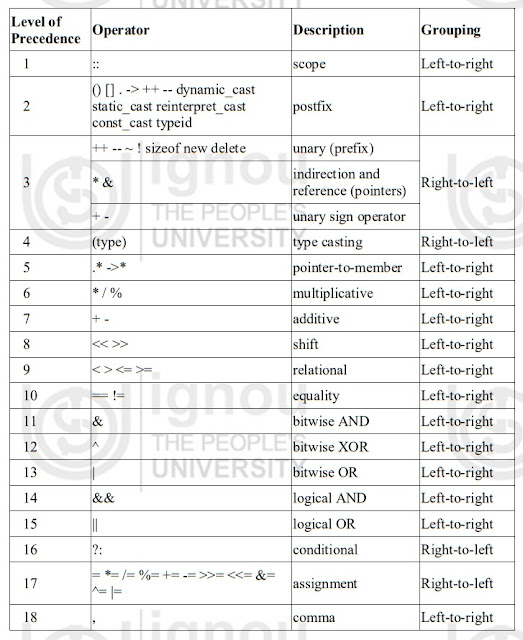 |
Precedence of operators in descending order |
Special Operators
Apart from the above operators that we have discussed above so far, C++ programming language supports some special operators. Some of them are: increment and decrement operator; size of operator; comma operator etc.
Increment and Decrement Operator
In C++ programming language, Increment and decrement operators can be used in two ways: they may either precede or follow the operand. The prefix version before the operand and postfix version comes after the operand. The two versions have the same effect on the operand, but they differ when they are applied in an expression. The prefix increment operator follows “change then use” rule and post fix operator follows “use then change” rule.
The size of operator
We know that different types of variables, constant, etc. require different amount of memory to store them. The sizeof operator can be used to find how many bytes are required for an object to store in memory.
Example:
sizeof (int) returns 2
sizeof (float) returns 4
if k is integer variable, the sizeof (k) returns 2.
The sizeof operator determines the amount of memory required for an object at compile time rather than at run time.
The comma operator
The comma operator gives left to right evaluation of expressions. It enables to put more than one expression separated by comma on a single line.
Example:
int i = 20, j = 25;
In the above statements, comma is used as a separator between the two statements.
Escape Sequence
There are some characters which can‟t be typed by keyboard in C++ programming language. These are called non-graphic characters. An escape sequence is represented by backslash (\) followed by one or more characters. The listing of common escape sequences.
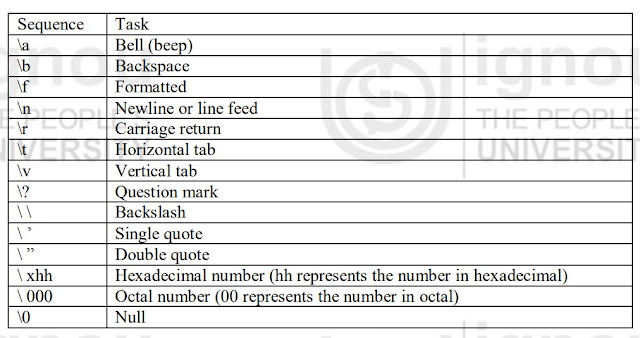 |
Escape Sequence |
Punctuators
In C++ programming language, following characters are used as punctuators for enhancing the readability and maintainability of programs.
 |
Punctuators |
ALSO SEARCH:
"operators in C++ language"
"operators in C++ language with examples"
"logical operators in C++ language"
"bitwise operators in C++ language"
"types of operators in C++ language"
"arithmetic operators in C++ language"
"explain different operators in C++ language"
"how many operators in C++ language"
"unary operators in C++ language"
"explain arithmetic and relational operators in C++ language"
"operators priority in C++ language"
"operators precedence in C++ language"
"operators and its types in C++ language"




