ERP systems have three limitations
1. Managers cannot generate custom reports and queries without help of computer programmer.
2. ERP system provides current status only such a open orders. It does not provide past record.
3. The data which is in the ERP application is not integrated with other enterprise or division lack of external intelligence.
ERP Related Technologies
There are many technologies that help to overcome these limitations. These technologies, when used in conjunction with the ERP package, help in overcoming the limitations of a standalone ERP system and thus, help the employees to make better decisions. Some of these technologies are:
- Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
- Management Information System (MIS)
- Decision Support Systems ( DSS)
- Executive Information Systems (EIS)
- Data warehousing
- Data Mining
- On-line Analytical Processing (OLAP)
- Supply Chain Management
Business Process Reengineering (BPR):
A Business process is a series of logically related task/activities performed to achieve a defined business outcome. Business process reengineering is design and analysis of workflows and processes within an organization. BPR is also known as Business Process Redesign, business transformation or business process change management.
BPR helps organizations fundamentally rethink how they do their work in order to dramatically improve customer service, cut operational costs.
BPR is basically redesigning/rethinking in a circular format using existing resources of an organization.
Advantages of BPR:
- It helps in integrating the various business processes of the organization.
- With good ERP package, the organization will be able to achieve dramatic improvements in areas such as cost, quality, speed, etc.
- Hence, many BPR initiatives are used in ERP implementation.
Management Information System (MIS):
MIS is a computer based system that optimizes the collection, collation, transfer and presentation of information throughout an organization, through an integrated structure of databases and information flow.
”MIS” described applications providing managers with information about sales, inventories, and other data that would help in managing the enterprise.
Over time, the term broadened to include: decision support systems, resource management and human resource management, enterprise resource planning (ERP), enterprise performance management (EPM), supply chain management (SCM), customer relationship management (CRM), project management and database retrieval applications.
Management information systems provide a variety of information products to managers.
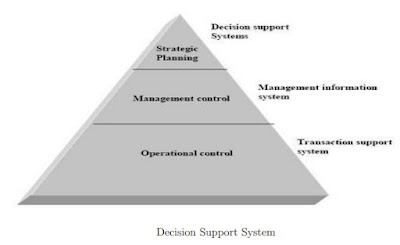
Decision Support System (DSS):
Decision support systems are interactive information systems that rely on an integrated set of user-friendly software and hardware tools, to produce and present information targeted to support management in the decision making process.
DSSs include knowledge-based systems. A properly designed DSS is an interactive software-based system intended to help decision makers compile useful information from a combination of raw data, documents, and personal knowledge, or business models to identify and solve problems and make decisions.
Three fundamental components of a DSS architecture are:
- the database (or knowledge base),
- the model (i.e., the decision context and user criteria), and
- the user interface.
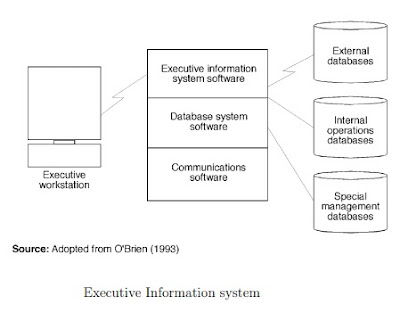
Executive Information System (EIS):
EIS is a decision support system especially made for senior level executives. An executive information system (EIS) is a type of management information system that facilitates and supports senior executive information and decision-making needs. It provides easy access to internal and external information relevant to organizational goals. It is commonly considered a specialized form of decision support system (DSS).
EIS are enterprise-wide DSS that help top-level executives analyze, compare, and highlight trends in important variables so that they can monitor performance and identify opportunities and problems. EIS and data warehousing technologies are converging in the marketplace.
Data warehousing:
A data warehouse or enterprise data warehouse (DW, DWH, or EDW) is a database used for reporting and data analysis.
Data warehouses store current as well as historical data and are used for creating trending reports for senior management reporting such as annual and quarterly comparisons.
This definition of the data warehouse focuses on data storage. The main source of the data is cleaned, transformed, catalogued and made available for use by managers and other business professionals for data mining, online analytical processing.
Data Mining:
Generally, data mining (sometimes called data or knowledge discovery) is the process of analyzing data from different perspectives and summarizing it into useful information - information that can be used to increase revenue, cuts costs, or both.
Data mining software is one of a number of analytical tools for analyzing data. It allows users to analyze data from many different dimensions or angles, categorize it, and summarize the relationships identified.
Technically, data mining is the process of finding correlations or patterns among dozens of fields in large relational databases.
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP):
OLAP (online analytical processing) is computer processing that enables a user to easily and selectively extract and view data from different points of view.
OLAP data is stored in a multidimensional database. Whereas a relational database can be thought of as two-dimensional, a multidimensional database considers each data attribute (such as product, geographic sales region, and time period) as a separate ”dimension.” OLAP software can locate the intersection of dimensions (all products sold in the Eastern region above a certain price during a certain time period) and display them. Attributes such as time periods can be broken down into sub attributes.
OLAP can be defined in five words Fast Analysis of Shared Multi-dimensional Information.
Supply Chain Management (SCM):
“ A supply chain is the alignment of firms that bring products or services to market."
Supply chain is a network of facilities and distribution options which perform the task of acquire of materials, transformation of these materials to finished products and distribution of these products to customers. Supply chain exists in service as well as manufacturing organizations.
ALSO SEARCH:
"ERP related technologies"
"different ERP related technologies"
"ERP and related technologies"
"explain ERP and related technologies"
"list out ERP related technologies"